Description  The glaucous gull is a large gull 25-30
inches in length with a wingspan of
60
inches. It has a white head, throat, breast, and belly and a gray back and wings. It has pale pink legs and feet and a yellow bill with a red tip. Males and females look alike. The glaucous gull is a large gull 25-30
inches in length with a wingspan of
60
inches. It has a white head, throat, breast, and belly and a gray back and wings. It has pale pink legs and feet and a yellow bill with a red tip. Males and females look alike.
Range 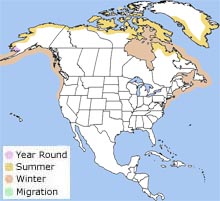 The glaucous gull breeds across the western and northern coasts of Alaska and across extreme northern Canada. It winters in the southern part of its breeding range and along the Pacific Coast south to California and along the Atlantic Coast south to Virginia.
It is also is found in small numbers in the Great Lakes and along the Gulf of Mexico. It is also found in Greenland, Iceland, and northern Europe and Asia. The glaucous gull breeds across the western and northern coasts of Alaska and across extreme northern Canada. It winters in the southern part of its breeding range and along the Pacific Coast south to California and along the Atlantic Coast south to Virginia.
It is also is found in small numbers in the Great Lakes and along the Gulf of Mexico. It is also found in Greenland, Iceland, and northern Europe and Asia.
Habitat
The glaucous gull is found on
lagoons, sea cliffs, ice pack, coastal tundra,
the shores of lakes and rivers, offshore islands, and the beach. It is also found in garbage dumps! |
|
Diet
The glaucous gull eats
a wide variety of food including
marine invertebrates, fish, the eggs and chicks of birds, and small birds and mammals. It also scavenges for carrion and garbage.
Life Cycle
 The glaucous gull nests in colonies on islands, at the edges of cliffs, on the tundra, at the edges of ponds and lakes, or on the beach. The male and the female build a nest of grass, twigs, moss, and sometimes feathers in a depression in the ground. The female lays 1-3 eggs. Both parents incubate the eggs for 28 days, and both parents care for and feed the chicks.
The chicks fledge when they are 45-50 days old but may stay with their parents until they migrate in the fall. The glaucous gull nests in colonies on islands, at the edges of cliffs, on the tundra, at the edges of ponds and lakes, or on the beach. The male and the female build a nest of grass, twigs, moss, and sometimes feathers in a depression in the ground. The female lays 1-3 eggs. Both parents incubate the eggs for 28 days, and both parents care for and feed the chicks.
The chicks fledge when they are 45-50 days old but may stay with their parents until they migrate in the fall.
Behavior
 The glaucous gull is a predator and a scavenger. It hunts for bird eggs and chicks in nesting areas, and it steals food from other birds. It is also a common visitor to garbage dumps, harbors, fish-processing plants, and sewage ponds. The glaucous gull is a predator and a scavenger. It hunts for bird eggs and chicks in nesting areas, and it steals food from other birds. It is also a common visitor to garbage dumps, harbors, fish-processing plants, and sewage ponds.
|



 The glaucous gull breeds across the western and northern coasts of Alaska and across extreme northern Canada. It winters in the southern part of its breeding range and along the Pacific Coast south to California and along the Atlantic Coast south to Virginia.
It is also is found in small numbers in the Great Lakes and along the Gulf of Mexico. It is also found in Greenland, Iceland, and northern Europe and Asia.
The glaucous gull breeds across the western and northern coasts of Alaska and across extreme northern Canada. It winters in the southern part of its breeding range and along the Pacific Coast south to California and along the Atlantic Coast south to Virginia.
It is also is found in small numbers in the Great Lakes and along the Gulf of Mexico. It is also found in Greenland, Iceland, and northern Europe and Asia.

