Description
 The American woodcock is
10-12
inches in length and has a
17-19
inch wingspan. It has a very long, straight bill; rounded wings; large, round black eyes set back in its head; a short tail; and short gray legs. It has a round head with three vertical black stripes and a plump, chunky body. It has a brown, black, and gray
plumage that looks like dead leaves and helps camouflage it in the brush. Males and females look alike, but females are usually a little larger. The American woodcock is
10-12
inches in length and has a
17-19
inch wingspan. It has a very long, straight bill; rounded wings; large, round black eyes set back in its head; a short tail; and short gray legs. It has a round head with three vertical black stripes and a plump, chunky body. It has a brown, black, and gray
plumage that looks like dead leaves and helps camouflage it in the brush. Males and females look alike, but females are usually a little larger.
Range 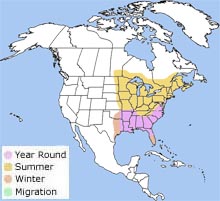 The American woodcock is found from
southeastern Manitoba, Canada east to Newfoundland, Canada and south to Texas and Florida. The American woodcock is found from
southeastern Manitoba, Canada east to Newfoundland, Canada and south to Texas and Florida.
Habitat
The American woodcock is found
in forests and thickets near open areas.
Diet
 The American woodcock probes in the dirt and leaves on the forest floor for earthworms. The tip of the American woodcock's bill is flexible. When the American woodcock probes in the dirt, the flexible end of the bill can open in the earth and grasp an earthworm! The American woodcock's main food source is earthworms, but it also eats insects, spiders, millipedes, centipedes, and larvae. The American woodcock probes in the dirt and leaves on the forest floor for earthworms. The tip of the American woodcock's bill is flexible. When the American woodcock probes in the dirt, the flexible end of the bill can open in the earth and grasp an earthworm! The American woodcock's main food source is earthworms, but it also eats insects, spiders, millipedes, centipedes, and larvae.
. | |
Life Cycle
 The male American woodcock courts the female using a
"peent" call that sounds like an insect buzzing. He then spirals up into the air and as he climbs, his wings make a whistling sound. Once he gets to about 200 feet in the air, he plummets down to the ground, letting out a musical twittering sound as he dives.
He uses a few display sites and tries to attract more than one female. The male may do his courtship display a number of times in a row. The male American woodcock courts the female using a
"peent" call that sounds like an insect buzzing. He then spirals up into the air and as he climbs, his wings make a whistling sound. Once he gets to about 200 feet in the air, he plummets down to the ground, letting out a musical twittering sound as he dives.
He uses a few display sites and tries to attract more than one female. The male may do his courtship display a number of times in a row.
 The female American woodcock usually lays 4 eggs, but she can lay as many as 12, in a shallow depression in the ground. The chicks hatch in 21-22 days and fledge when they are 19-21 days old. The female American woodcock usually lays 4 eggs, but she can lay as many as 12, in a shallow depression in the ground. The chicks hatch in 21-22 days and fledge when they are 19-21 days old.
 The chicks leave the nest shortly after hatching, but they cannot feed themselves for 3-4 days - their mother feeds them for the first week.
They can fly short distances by the time they are two weeks old. At two weeks old they have also learned how to freeze in place when threatened. The chicks stay in the nesting area until they migrate in the fall.
In the wild, the American woodcock has a life span of up to eight years. The chicks leave the nest shortly after hatching, but they cannot feed themselves for 3-4 days - their mother feeds them for the first week.
They can fly short distances by the time they are two weeks old. At two weeks old they have also learned how to freeze in place when threatened. The chicks stay in the nesting area until they migrate in the fall.
In the wild, the American woodcock has a life span of up to eight years.
Behavior
 The American woodcock's coloration makes it almost impossible to spot in the wild. It is a solitary bird and is most active after dusk. It even migrates at night, alone or in very small groups.
The American woodcock is also known as the timberdoodle and the night partridge. The American woodcock's coloration makes it almost impossible to spot in the wild. It is a solitary bird and is most active after dusk. It even migrates at night, alone or in very small groups.
The American woodcock is also known as the timberdoodle and the night partridge.
|



 The American woodcock is found from
southeastern Manitoba, Canada east to Newfoundland, Canada and south to Texas and Florida.
The American woodcock is found from
southeastern Manitoba, Canada east to Newfoundland, Canada and south to Texas and Florida.




